
Image Source: Needpix
The pursuit of efficiency and quality is relentless. Integrating Design of Experiments (DOE) principles into Lean Manufacturing practices offers a groundbreaking approach to this quest. This synergy streamlines production processes, enhances product quality, fosters innovation, and drives continuous improvement.
In this blog, we delve into the intricate ways in which DOE principles magnify the effectiveness of Lean Manufacturing. We’ll explore how DOE’s systematic approach to experimentation and data analysis unlocks new levels of efficiency and productivity. From optimizing process parameters to reducing costs, each section of our discussion will shed light on the transformative impact of DOE on Lean Manufacturing practices.
Understanding the Fundamentals: DOE Principles and Lean Manufacturing
Here’s a summary of the key concepts:
- Design of Experiments (DOE) Principles: DOE is a statistical approach for planning and conducting experiments to evaluate the effects of various factors on a specific outcome. It helps understand the cause-and-effect relationships in a process or product, allowing for optimization and improved quality control.
- Lean Manufacturing: This methodology aims to streamline production by minimizing waste and increasing efficiency. Originating from the Toyota Production System, it focuses on eliminating non-value-adding activities, improving process flow, maintaining high quality, and encouraging continuous improvement.
Integrating DOE principles with Lean Manufacturing enables businesses to enhance operational efficiency and product quality through systematic experimentation and data-driven decision-making. This combination is key in optimizing manufacturing processes and providing maximum value to customers.
How DOE Elevates Lean Manufacturing
In the fusion of Design of Experiments (DOE) principles with Lean Manufacturing, we witness a powerful convergence of statistical rigor and efficiency-driven philosophy. This blend enhances manufacturing processes and redefines production quality standards and cost-effectiveness.
1. Optimization of Process Parameters
The heart of Lean Manufacturing lies in its relentless pursuit of eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency. DOE principles play a pivotal role in achieving this by enabling a precise understanding of how different factors affect the manufacturing process. It’s not just about tweaking variables; it’s about knowing which adjustments will yield the most significant improvements.
DOE achieves this through systematic experimentation. By exploring a range of conditions and variables, manufacturers can ascertain the optimal settings for their processes. For instance, when factors like temperature, material mix, and machine speed influence the final product’s quality, DOE helps identify the perfect combination that maximizes output quality while minimizing resource use.
This approach contrasts starkly with traditional trial-and-error methods. Instead of making changes based on assumptions or limited data, DOE relies on statistical analysis to guide decisions. This ensures that every modification in the manufacturing process is data-driven, leading to consistent and predictable improvements in efficiency and productivity.
2. Enhanced Product Quality
Quality is the cornerstone of Lean Manufacturing, and here, DOE shines brightly. The methodology’s ability to isolate and analyze the impact of individual variables on the overall process enables manufacturers to fine-tune their operations for superior quality output.

Image Source: Needpix
For example, consider a production line for electronic components, where factors like solder temperature, conveyor speed, and ambient humidity can affect the quality of the final product.
Through DOE, manufacturers can determine how each of these variables and their interactions influence the defect rate. This understanding allows for adjustments targeting quality improvements, such as reducing soldering defects or improving component longevity.
The statistical nature of DOE also plays a crucial role in quality control. Manufacturers can discern between random fluctuations and genuine trends by analyzing the variance in experiments. This distinction is crucial for making informed decisions that enhance product quality. Moreover, DOE’s structured approach reduces the risk of overlooking subtle yet critical interactions between variables, which can profoundly impact the final product quality.
3. Cost Reduction through Precision
Lean Manufacturing is synonymous with cost efficiency, striving to reduce waste in all forms. DOE complements this by offering a precise, data-driven approach to identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses in the manufacturing process. This methodical approach goes beyond cost-cutting; it’s about smart resource allocation and maximizing value.

Image Source: Unsplash
For instance, consider a manufacturing process where material costs contribute significantly to the overall expenses. A company can systematically test various material compositions and quantities through DOE to determine the most cost-effective combination that meets quality standards. This could lead to significant savings without compromising product integrity.
Moreover, DOE’s ability to reveal the most influential factors in a process helps manufacturers focus their resources on areas with the highest return. This targeted approach to process improvement can lead to substantial cost savings.
For example, if DOE shows that a slight increase in a particular raw material’s quality can significantly enhance product durability, the investment in higher-quality materials could reduce the long-term costs associated with returns and warranty claims.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making and Continuous Improvement
The essence of Lean Manufacturing is continuous improvement, and DOE is a tool that feeds this endless cycle of enhancement. With its foundation in statistical analysis, DOE enables manufacturers to make decisions based on complex data rather than intuition or guesswork.
This data-driven approach allows for more accurate predictions and informed choices. For example, when faced with a production bottleneck, DOE can be used to experiment with different process configurations to identify the most effective solution. The resulting data provides a solid basis for decision-making, ensuring that changes to the process are both beneficial and sustainable.
Furthermore, the insights gained from DOE are not static; they fuel a culture of ongoing learning and adaptation. As market conditions, material properties, or production technologies evolve, DOE can be reapplied to reassess and refine processes. This ensures that manufacturing operations remain agile and responsive to changing demands, maintaining efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
5. Faster Time to Market
Reducing the time it takes to bring a product from concept to customer is a critical competitive advantage. Here, the integration of DOE with Lean Manufacturing principles significantly accelerates product development and process optimization.
Image Source: Needpix
DOE’s structured approach to experimentation allows for simultaneous testing of multiple variables, providing a comprehensive understanding of their effects in a shorter timeframe. This multi-faceted analysis can rapidly identify the best conditions for manufacturing, thus speeding up the process of finalizing product designs and production methods.
For example, in developing a new automotive part, DOE can be used to quickly ascertain the optimal combination of materials and manufacturing conditions that meet both quality and safety standards. Manufacturers can avoid the lengthy trial-and-error processes that often delay market entry by conducting these experiments early in the product development phase.
6. Continuous Improvement
The philosophy of continuous improvement is at the core of Lean Manufacturing, and DOE is a potent tool in this ongoing quest for excellence. DOE facilitates a systematic approach to testing and refining manufacturing processes, ensuring that improvements are based on solid data and not just sporadic adjustments.
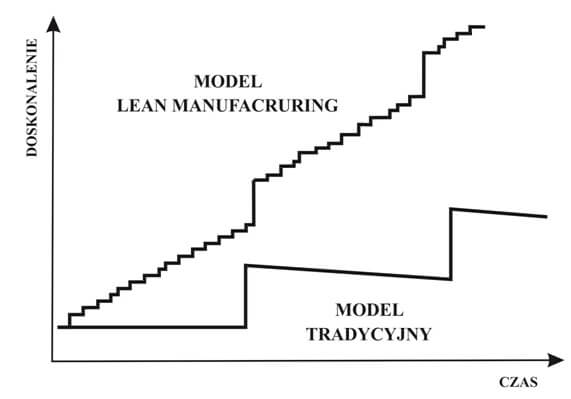
Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
This approach aligns with the Lean principle of ‘Kaizen,’ or continuous change for the better. DOE provides a framework for identifying areas of improvement, testing hypotheses, and implementing changes in a controlled manner. This systematic approach to problem-solving ensures that changes lead to tangible, measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
For instance, in a production line, continuous application of DOE can lead to incremental improvements in machine settings, worker performance, and material usage. Over time, these minor adjustments accumulate, significantly enhancing overall production efficiency and product quality.
Conclusion
The synergy between Design of Experiments (DOE) and Lean Manufacturing marks a significant stride in industrial efficiency and quality enhancement. This integration streamlines processes and injects a robust, data-driven approach into the heart of manufacturing.
It fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, ensuring that manufacturing systems are responsive and adaptable to evolving demands and technologies. Therefore, the combined force of DOE and Lean Manufacturing is a beacon for industries aiming to achieve peak performance and sustainability in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Transform your production processes today! Discover the powerful combination of DOE and Lean Manufacturing in our Operational Design of Experiments Course. Gain the skills to make data-driven decisions and improve your manufacturing operations. Enroll today!


